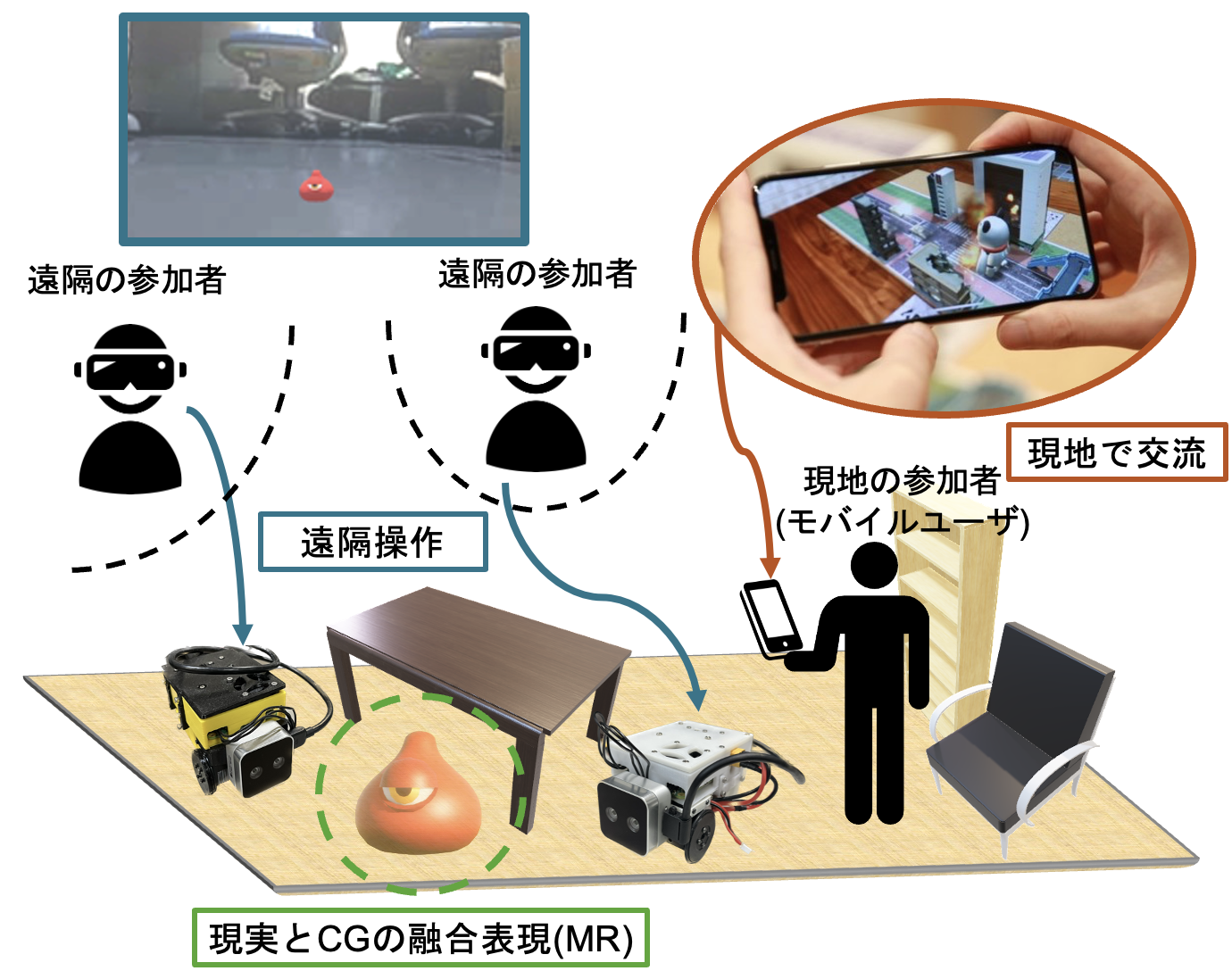
Ritsumei Real-World Robotic Metaverse (R-Metaverse)

Three Features
R-Metaverse has three key features:
-
Remote Operation
Remote participants (robot users) can wear HMDs and operate telepresence robots remotely.
-
Integration of Reality and CG (MR)
Through Mixed Reality (MR), users can not only view video from remote locations but also experience 3DCG overlays, creating a fusion of reality and computer graphics.
-
On-site Interaction
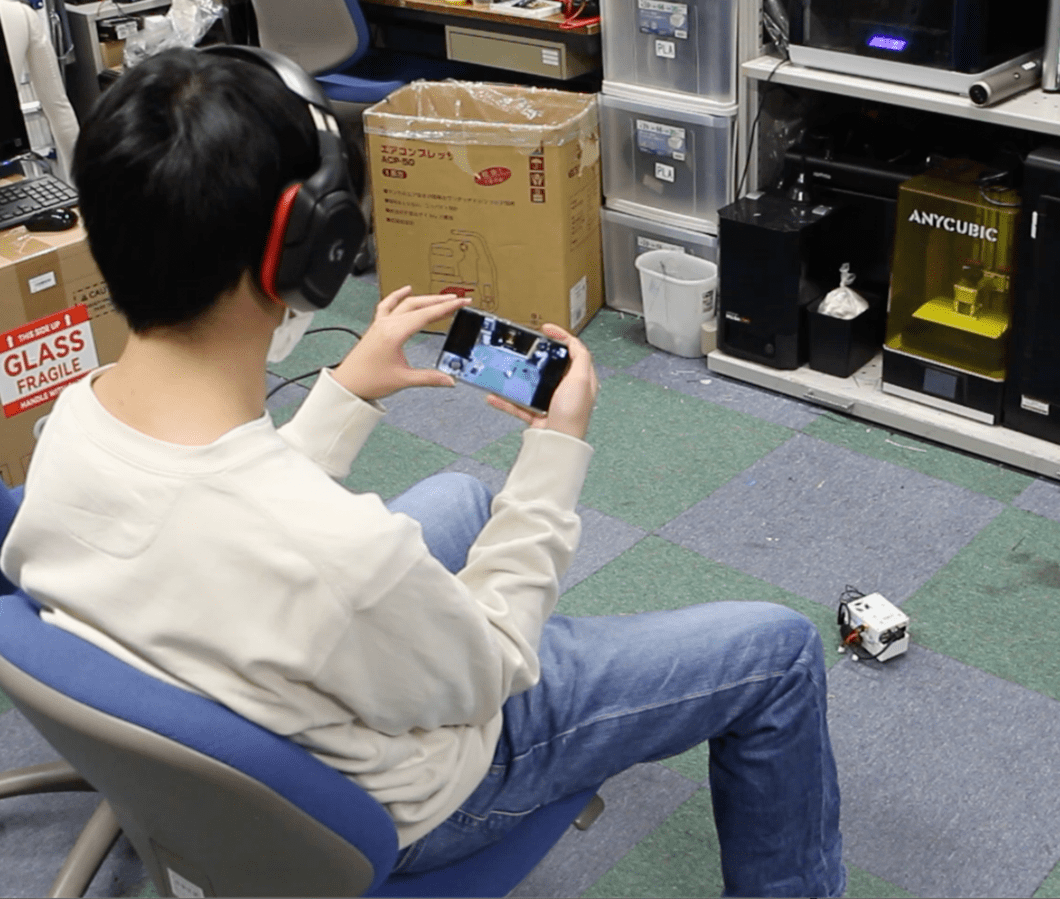
People at the physical location (mobile users) can use smartphones to view the MR experience of users operating the telepresence robots, enabling interaction between on-site and remote participants.
Research Background
In recent years, content using virtual spaces built on computers, known as metaverse, has gained attention. By using HMDs (Head-Mounted Displays), the metaverse enables users to experience virtual spaces with a sense of presence through virtual avatars, as if they were actually inside the virtual space. Furthermore, when this space is connected to a network, it allows people to interact as if they were talking in person, ignoring physical constraints of distance.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on promoting remote work practices in businesses, an increase in metaverse-based services is anticipated in the future. However, experiencing 3D virtual spaces used in the metaverse requires significant costs. The costs mentioned here refer to the effort required to create spaces, the computation needed to render spaces, and the collision detection calculations necessary when experiencing these spaces. Additionally, the adoption rate of VR goggles is less than 10%, and there’s a limitation where experiences are confined only to users wearing HMDs. To address these issues, we propose “Ritsumei Real-World Robotic Metaverse (R-Metaverse),” a new form of metaverse that utilizes remotely operated robots and real physical spaces.
System Configuration
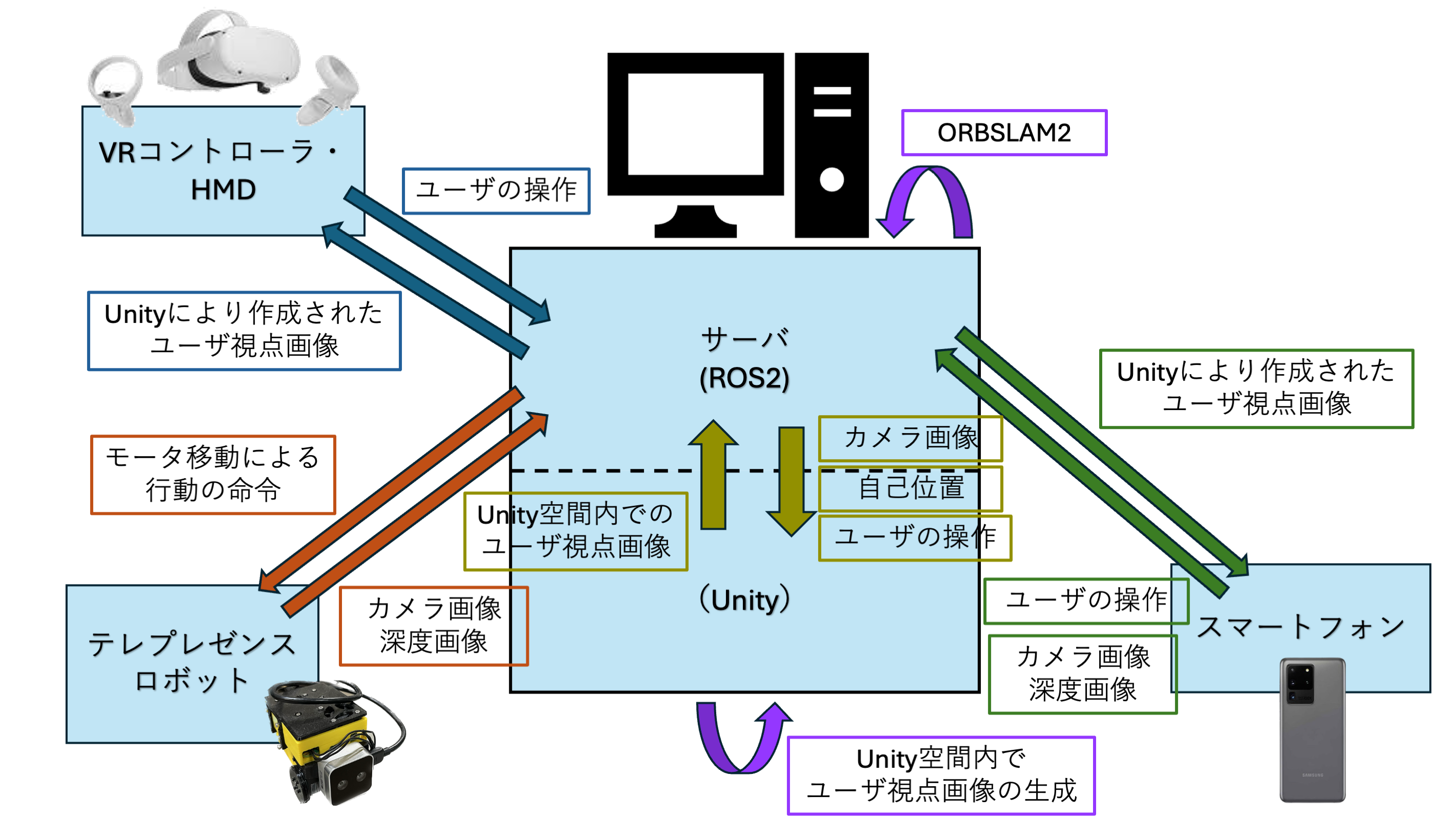
In R-Metaverse, ROS2 is used for data transmission and processing between devices. Unity is used to implement the Mixed Reality (MR) experience.
Using Visual SLAM technology called ORBSLAM2, images obtained from smartphones or robots are processed in real-time to estimate the position and orientation of each camera in the physical space. The position and orientation data obtained from ORBSLAM2 is utilized to implement MR functionality.
Telepresence Robot
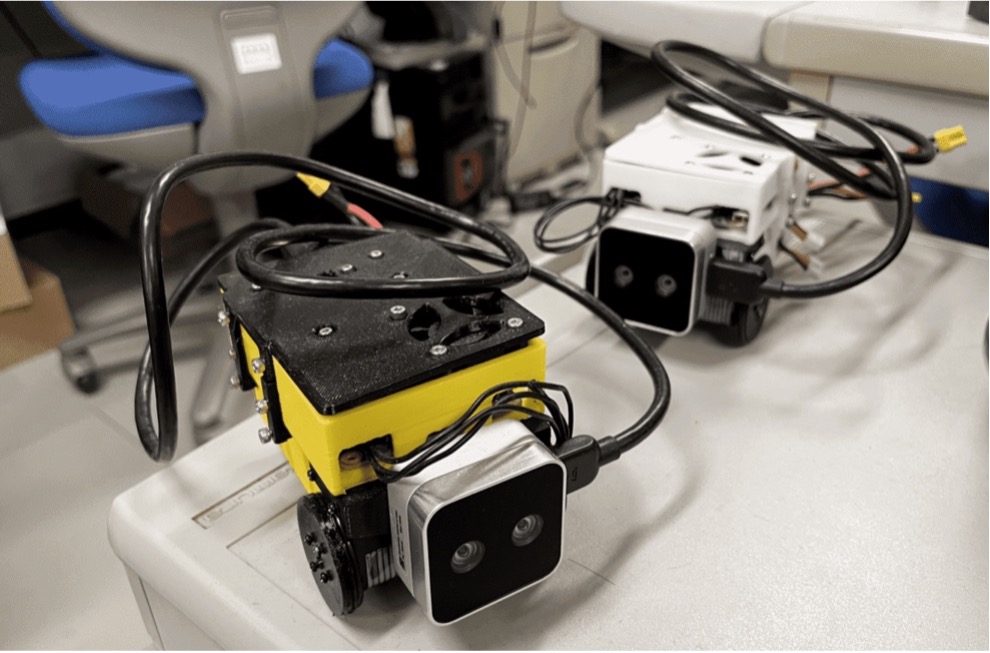
The telepresence robot is a palm-sized small robot measuring 80mm in width, 125mm in depth, 72mm in height, and weighing 450g. This allows users to experience moving through the real world in a miniaturized body scaled to the robot’s size, enabling them to enjoy experiences in spaces that are normally inaccessible, such as under floors or in ceiling cavities.
System
In online communication, the degree to which one feels “the other person is there, the other person is nearby” is called social presence. Social presence is higher in media that can convey non-verbal information such as facial expressions and gestures, leading to better communication. Therefore, in today’s increasing demand for online communication, it is important to develop systems that can convey non-verbal information with awareness of social presence to build good relationships.
Mobile User’s Facial Expression Confirmation System
This system allows robot users who remotely operate robots to check the facial expressions of mobile users participating via smartphones. This enables robot users to feel closer to mobile users who are actually at a distance. The facial expressions are displayed at the top of the robot user’s view screen.
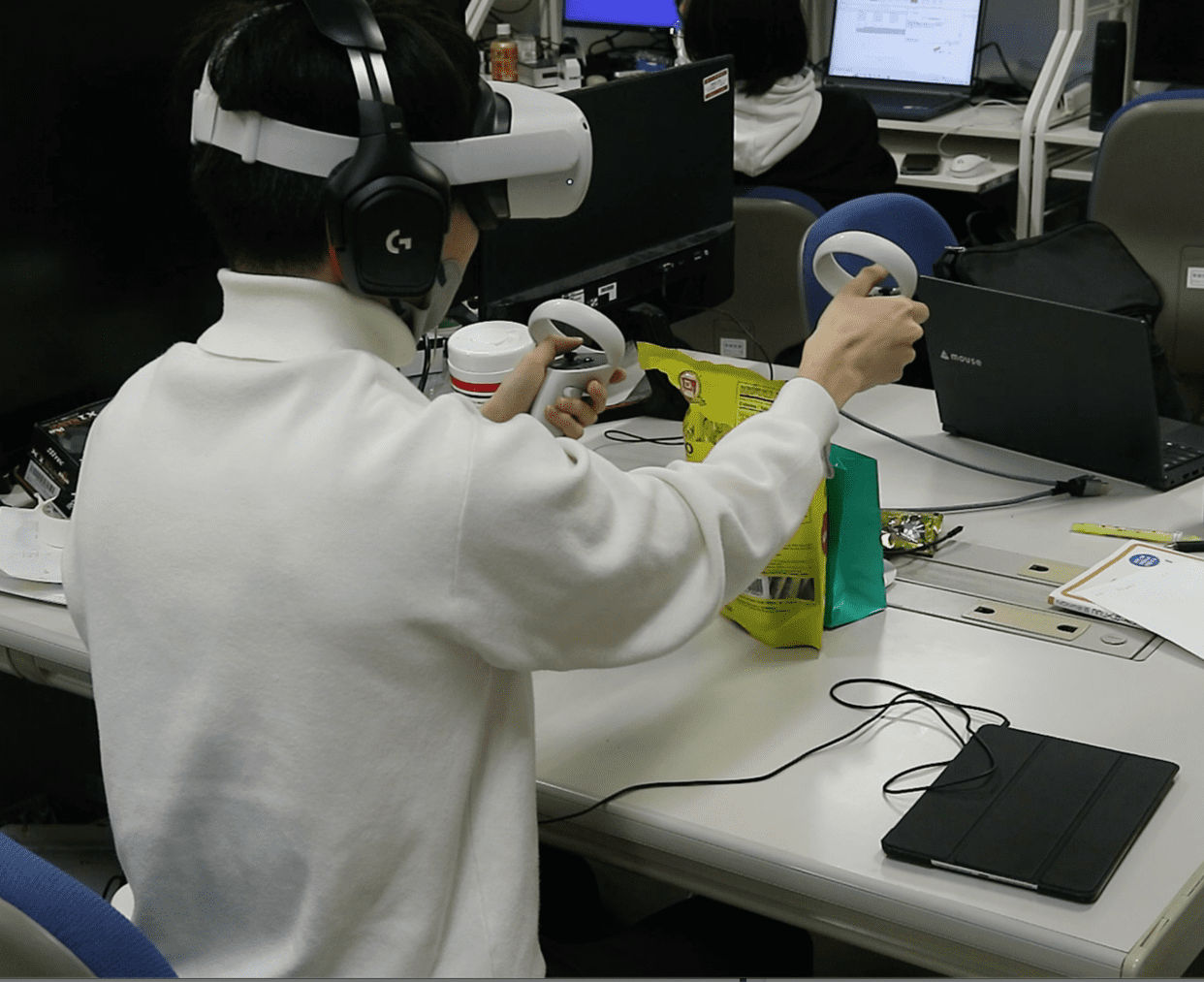

Robot User Avatar Confirmation System
This system allows mobile users participating via smartphones to see the gestures of robot users who are remotely operating robots, such as head and hand movements. This enables mobile users to feel closer to robot users who are actually remote. When a mobile user points their smartphone at the robot, an avatar synchronized with the robot user’s movements is displayed. Additionally, in the lower left corner of the screen, users can see how their own facial expressions are being captured (Mobile User’s Facial Expression Confirmation System).
